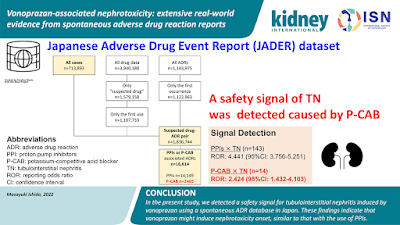
A new agent has been found to cause AKI and AIN—Vonoprazan. A recent paper in Kidney International is the first to describe this from Japan. The authors used the National reporting database of drug toxicities in Japan to assess this and compared it to PPIs—JADER database. See visual ab from the recent paper.
What is vonoprazan?
Vonoprazan, a
potassium-competitive acid blocker possessing a new mechanism of action.
Vonoprazan inhibits acid secretion in the cells of the gastric wall. The
inhibitory effect of vonoprazan on H+, K+-ATPase is perhaps over 300 times
greater than that of lansoprazole.
In Japan, this drug was approved for use for acid reflux in 2015. In the US, this drug has been FDA approved for esophageal esophagitis in association with H pylori recently in May 2022. A recent meta-analysis also found that vonoprazan is non inferior to PPIs as therapy for GERD but in the subgroup for severe erosive esophagitis- it was more effective.
The mechanism of action of vonoprazan is that it competes with potassium ions for the reversible inhibition of H+- K+-ATPase, whereas PPIs act by binding covalently to the gastric H+, K+-ATPase via disulfide bonds. Having a H+, K+-ATPASe in the kidney have any impact? Not sure?
Another interesting finding from another study showed
increase tacrolimus levels when this agent is used- a caution in our GN and
transplant patients.
As we learn more about this agent in the US, we need to be vigilant!

No comments:
Post a Comment